Classification & CV Example
Yeon Soo, Choi
Application with Default Data
ISLR 패키지의 Default 데이터를 이용해 전처리 및 EDA 과정은 생략하고 공부한 Classification 모델의 구현 그리고 Cross-Validation 의 과정까지 포함해 모델을 적합하여 성능을 비교하는 실습을 진행하였다.
library(ISLR)
library(knitr)
library(ggplot2)
library(caret)
## Loading required package: lattice
library(MASS)
Defaut 데이터는 income 과 balance 그리고 종속변수로서 부도 여부에 대한 정보를 제공하는 default 변수를 포함하고 있다.
dim(Default)
## [1] 10000 4
kable(head(Default))
| default | student | balance | income |
|---|---|---|---|
| No | No | 729.5265 | 44361.625 |
| No | Yes | 817.1804 | 12106.135 |
| No | No | 1073.5492 | 31767.139 |
| No | No | 529.2506 | 35704.494 |
| No | No | 785.6559 | 38463.496 |
| No | Yes | 919.5885 | 7491.559 |
종속변수가 'Yes' , 'No' 로 Binary Classification 문제이기 때문에 적절한 분류 모형의 선택과 복잡도를 Cross-Validation (10-Fold) 과정을 통해 보정과 함께 최적화하는 과정을 진행할 것이다.
독립변수인 income 과 balance 를 모두 사용하여 default 에 대한 예측을 위한 분류 모형으로 공부한 Logistic Regression Model, LDA, QDA, KNN 들을 고려하였다.
Fitting Logistic Regerssion Model
10-Fold CV 로 모델의 성능을 추정할 것이므로 이를 진행하고 모델 적합을 실시한다.
set.seed(2013122044)
# define training control
train_control= trainControl(method="cv", number=10)
logistic=train(default~.,data=Default,trControl=train_control,method='glm')
logistic
## Generalized Linear Model
##
## 10000 samples
## 3 predictor
## 2 classes: 'No', 'Yes'
##
## No pre-processing
## Resampling: Cross-Validated (10 fold)
## Summary of sample sizes: 9000, 8999, 9000, 9000, 9000, 9000, ...
## Resampling results:
##
## Accuracy Kappa
## 0.9730992 0.4202143
summary(logistic)
##
## Call:
## NULL
##
## Deviance Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -2.4691 -0.1418 -0.0557 -0.0203 3.7383
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept) -1.087e+01 4.923e-01 -22.080 < 2e-16 ***
## studentYes -6.468e-01 2.363e-01 -2.738 0.00619 **
## balance 5.737e-03 2.319e-04 24.738 < 2e-16 ***
## income 3.033e-06 8.203e-06 0.370 0.71152
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## (Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 1)
##
## Null deviance: 2920.6 on 9999 degrees of freedom
## Residual deviance: 1571.5 on 9996 degrees of freedom
## AIC: 1579.5
##
## Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 8
모형 적합 결과 income 변수가 유의하지 않다는 결과가 확인되어 이를 제하고 다시 모형을 적합하였다.
## logistic regression
logistic=train(default~student+balance, data=Default,trControl=train_control,method='glm')
logistic
## Generalized Linear Model
##
## 10000 samples
## 2 predictor
## 2 classes: 'No', 'Yes'
##
## No pre-processing
## Resampling: Cross-Validated (10 fold)
## Summary of sample sizes: 9000, 9000, 8999, 9001, 9000, 9000, ...
## Resampling results:
##
## Accuracy Kappa
## 0.9732002 0.4223812
summary(logistic)
##
## Call:
## NULL
##
## Deviance Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -2.4578 -0.1422 -0.0559 -0.0203 3.7435
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept) -1.075e+01 3.692e-01 -29.116 < 2e-16 ***
## studentYes -7.149e-01 1.475e-01 -4.846 1.26e-06 ***
## balance 5.738e-03 2.318e-04 24.750 < 2e-16 ***
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## (Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 1)
##
## Null deviance: 2920.6 on 9999 degrees of freedom
## Residual deviance: 1571.7 on 9997 degrees of freedom
## AIC: 1577.7
##
## Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 8
적합 결과 분류 모델의 성능을 확인해보자.
## predictions
pred_logistic=predict(logistic,Default)
#type='prob'
## confusion matrix
kable(table(pred_logistic,Default$default))
| No | Yes | |
|---|---|---|
| No | 9628 | 228 |
| Yes | 39 | 105 |
## estimated test error rate from 10-fold CV
estimated_test_error_logistic=1-logistic$results[,2]
## ROC Curve
library(ROCR)
## Loading required package: gplots
##
## Attaching package: 'gplots'
## The following object is masked from 'package:stats':
##
## lowess
prediction=prediction(predict(logistic,Default,type='prob')[,2],Default$default)
perf_AUC=performance(prediction,"auc")
AUC_logistic=perf_AUC@y.values[[1]]
perf_ROC=performance(prediction,"tpr","fpr")
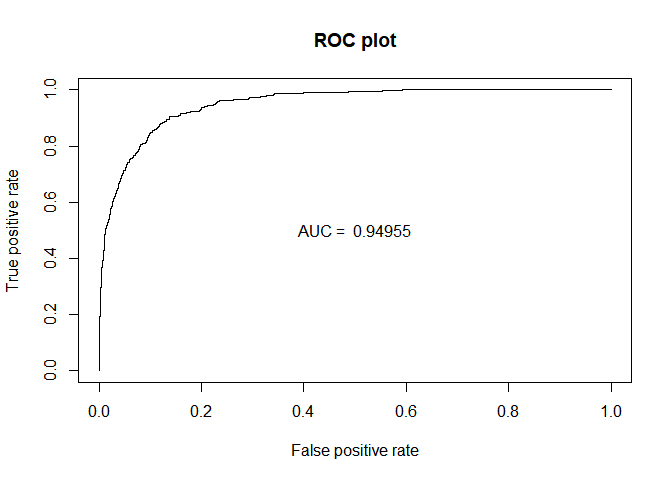
plot(perf_ROC, main="ROC plot")
text(0.5,0.5,paste("AUC = ",format(AUC_logistic, digits=5, scientific=FALSE)))
Fitting LDA
## lda
lda=train(default~student+balance, data=Default,trControl=train_control,method='lda')
lda
## Linear Discriminant Analysis
##
## 10000 samples
## 2 predictor
## 2 classes: 'No', 'Yes'
##
## No pre-processing
## Resampling: Cross-Validated (10 fold)
## Summary of sample sizes: 8999, 8999, 9000, 9000, 8999, 9001, ...
## Resampling results:
##
## Accuracy Kappa
## 0.9725012 0.3481767
적합 결과 분류 모델의 성능을 확인해보자.
## predictions
pred_lda=predict(lda,Default)
#type='prob'
## confusion matrix
kable(table(pred_lda,Default$default))
| No | Yes | |
|---|---|---|
| No | 9644 | 252 |
| Yes | 23 | 81 |
## estimated test error rate from 10-fold CV
estimated_test_error_lda=1-lda$results[,2]
## ROC Curve
library(ROCR)
prediction=prediction(predict(lda,Default,type='prob')[,2],Default$default)
perf_AUC=performance(prediction,"auc")
AUC_lda=perf_AUC@y.values[[1]]
perf_ROC=performance(prediction,"tpr","fpr")
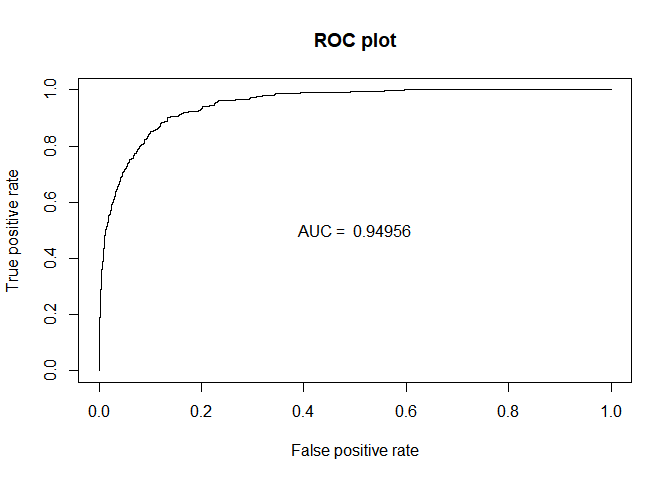
plot(perf_ROC, main="ROC plot")
text(0.5,0.5,paste("AUC = ",format(AUC_lda, digits=5, scientific=FALSE)))
Fitting QDA
실제 Decision Boundary가 선형이 아닐 경우, 즉 더 복잡한 모델의 경우인 QDA 적합을 시도하였다.
## lda
qda=train(default~student+balance, data=Default,trControl=train_control,method='qda')
qda
## Quadratic Discriminant Analysis
##
## 10000 samples
## 2 predictor
## 2 classes: 'No', 'Yes'
##
## No pre-processing
## Resampling: Cross-Validated (10 fold)
## Summary of sample sizes: 9000, 8999, 9001, 9000, 9000, 9001, ...
## Resampling results:
##
## Accuracy Kappa
## 0.972799 0.3785879
적합 결과 분류 모델의 성능을 확인해보자.
## predictions
pred_qda=predict(qda,Default)
#type='prob'
## confusion matrix
kable(table(pred_qda,Default$default))
| No | Yes | |
|---|---|---|
| No | 9637 | 244 |
| Yes | 30 | 89 |
## estimated test error rate from 10-fold CV
estimated_test_error_qda=1-qda$results[,2]
## ROC Curve
library(ROCR)
prediction=prediction(predict(qda,Default,type='prob')[,2],Default$default)
perf_AUC=performance(prediction,"auc")
AUC_qda=perf_AUC@y.values[[1]]
perf_ROC=performance(prediction,"tpr","fpr")
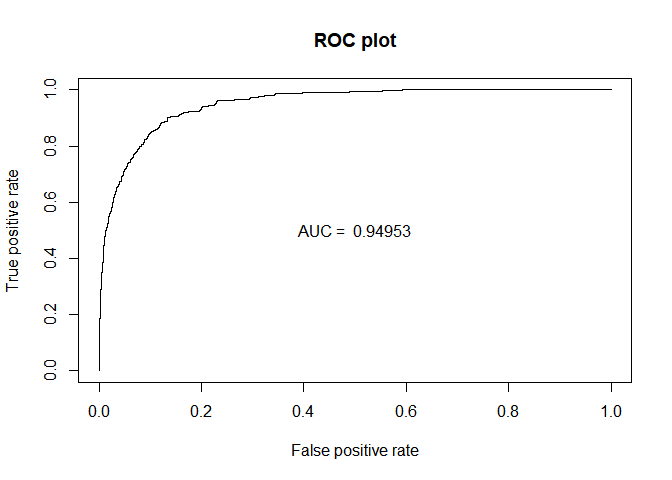
plot(perf_ROC, main="ROC plot")
text(0.5,0.5,paste("AUC = ",format(AUC_qda, digits=5, scientific=FALSE)))
Fitting KNN
k값을 1에서 100까지 조절해가며 KNN 적합 또한 시도하였다.
caret 패키지에서는 k-Fold Cross Validation 까지 진행하며 Accuracy가 가장 큰 K값 또한 찾아주기 때문에 이를 이용해 K=9 값을 이용하여 계산하였다.
## KNN
knn=train(default~student+balance, data=Default,trControl=train_control,method='knn')
knn
## k-Nearest Neighbors
##
## 10000 samples
## 2 predictor
## 2 classes: 'No', 'Yes'
##
## No pre-processing
## Resampling: Cross-Validated (10 fold)
## Summary of sample sizes: 9000, 9000, 9000, 9000, 9000, 9000, ...
## Resampling results across tuning parameters:
##
## k Accuracy Kappa
## 5 0.9683000 0.3893633
## 7 0.9707002 0.3999523
## 9 0.9717003 0.4158985
##
## Accuracy was used to select the optimal model using the largest value.
## The final value used for the model was k = 9.
적합 결과 분류 모델의 성능을 확인해보자.
## predictions
pred_knn=predict(knn,Default)
#type='prob'
## confusion matrix
kable(table(pred_knn,Default$default))
| No | Yes | |
|---|---|---|
| No | 9620 | 218 |
| Yes | 47 | 115 |
## estimated test error rate from 10-fold CV
estimated_test_error_knn=1-knn$results[3,2]
## ROC Curve
library(ROCR)
prediction=prediction(predict(knn,Default,type='prob')[,2],Default$default)
perf_AUC=performance(prediction,"auc")
AUC_knn=perf_AUC@y.values[[1]]
perf_ROC=performance(prediction,"tpr","fpr")
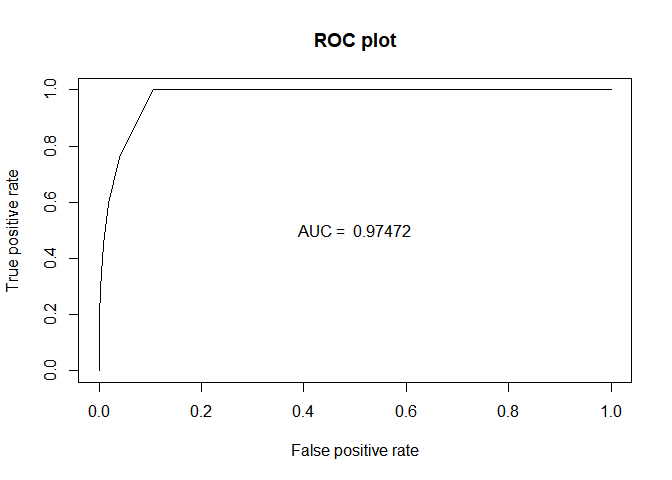
plot(perf_ROC, main="ROC plot")
text(0.5,0.5,paste("AUC = ",format(AUC_knn, digits=5, scientific=FALSE)))
지금까지 적합한 모델들의 성능을 비교해본 결과는 다음과 같다.
Accuracy (Estimated Test Error Rate)
error_rate_final=data.frame(Logistic=estimated_test_error_logistic,LDA=estimated_test_error_lda,QDA=estimated_test_error_qda,KNN=estimated_test_error_knn)
kable(error_rate_final)
| Logistic | LDA | QDA | KNN |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0267998 | 0.0274988 | 0.027201 | 0.0282997 |
오차율의 측면에서는 CV 결과 로지스틱 회귀 모형의 성능이 가장 좋았다.
결국 실제 decision boundary 들이 선형으로 설명될 수 있는 간단한 모형이 적절하다는 것이다.
따라서 이 데이터를 가지고 복잡한 모형들을 적합시켰을 때 오히려 모형의 성능이 더 좋지 않았을 것이라고 짐작 가능하다.
하지만, Confusion Matrix 를 기반으로한 ROC Curve 그리고 AUC 를 통해서 본 결과는 조금 다르다.
Confusion Matrix, ROC, AUC
auc_final=data.frame(Logistic=AUC_logistic,LDA=AUC_lda,QDA=AUC_qda,KNN=AUC_knn)
kable(auc_final)
| Logistic | LDA | QDA | KNN |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.9495476 | 0.9495584 | 0.9495317 | 0.9747236 |
AUC 의 값은 KNN 의 값이 가장 높다. 하지만 이 또한 train 하에서 계산된 값이기 때문에 절대 정확하다고 할 수 없다.
전체적인 오차율보다는 공부한 민감도와 False Positive Rate 까지 고려했을 때 좋은 모형은 무엇일까라는 의문이 들어 이에 대해 쓰이는 지표 중에 하나인 F1 Score 를 찾을 수 있었다.
따라서 이 지표에 대해 10-Fold CV 까지 진행한 결과 최적의 모델이 무엇인지 확인하기 위해 F1-Score 가 최대화되는 모델을 찾는 과정을 수행하였다.
library(MLmetrics)
##
## Attaching package: 'MLmetrics'
## The following objects are masked from 'package:caret':
##
## MAE, RMSE
## The following object is masked from 'package:base':
##
## Recall
##f1 score
f1=function(data, lev = NULL, model = NULL) {
f1_val=F1_Score(y_pred = data$pred, y_true = data$obs)
c(F1 = f1_val)
}
##
train_control= trainControl(method="cv", number=10,summaryFunction=f1)
## logistic
logistic=train(default~student+balance, data=Default,trControl=train_control,method='glm',metric='F1')
f1_logistic=logistic$results[,2]
## lda
lda=train(default~student+balance, data=Default,trControl=train_control,method='lda',metric='F1')
f1_lda=lda$results[,2]
## qda
qda=train(default~student+balance, data=Default,trControl=train_control,method='qda',metric='F1')
f1_qda=qda$results[,2]
## knn
knn=train(default~student+balance, data=Default,trControl=train_control,method='knn',metric='F1')
f1_knn=knn$results[3,2]
f1_final=data.frame(Logistic=f1_logistic,LDA=f1_lda,QDA=f1_qda,KNN=f1_knn)
kable(f1_final)
| Logistic | LDA | QDA | KNN |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.9863772 | 0.9859941 | 0.9860356 | 0.9855377 |
최종적으로 F1-Score 의 경우에도 로지스틱 회귀 모형이 가장 성능이 좋다는 것을 확인할 수 있다.